详细描述
Specifications
1206E-E66TA Industrial Engine
BK (Engine)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()

Important Safety Information
Most accidents tha t involve produc t op eration, ma intena nc e and repair are caus ed by failure to
ob serve basic safety rules or precautions . An accident can often be avoided by recog nizing pote ntially
ha za rdous situations before an accident oc curs . A person mus t be alert to pote ntial ha za rds. This
person should also ha ve the ne cessary training, skills and tools to perform the se func tions properly.
Improper operation, lubrication, maintenance or repair of this product can be dangerous and
could result in injury or death.
Do not operate or perform any lubrication, maintenance or repair on this product, until you have
read and understood the operation, lubrication, maintenance and repair information.
Sa fety precautions and warning s are provided in this ma nua l and on the produc t. If the se ha za rd
warning s are not he eded, bod ily injury or death could oc cur to you or to othe r persons .
The ha za rds are identified by the “Safety Alert Symb ol” and followed by a “Signa l Word” suc h as
“DANGER”, “WARNING” or “CAUTION”. The Sa fety Alert “WARNING” label is shown below.
The me aning of this safety alert symb ol is as follows:
Attention! Become Alert! Your Safety is Involved.
The me ssage tha t appears und er the warning explains the ha za rd and can be either written or
pictorially presente d.
Op erations tha t ma y caus e produc t dama ge are identified by “NOTICE” labels on the produc t and in
this pub lication.
Perkins cannot anticipate every possible circumstance that might involve a potential hazard. The
warnings in this publication and on the product are, therefore, not all inclusive. If a tool, procedure,
work method or operating technique that is not specifically recommended by Perkins is used,
you must satisfy yourself that it is safe for you and for others. You should also ensure that the
product will not be damaged or be made unsafe by the operation, lubrication, maintenance or
repair procedures that you choose.
The informa tion, specifications , and illustrations in this pub lication are on the basis of informa tion tha t
was available at the time tha t the pub lication was written. The specifications , torque s, pressure s,
me asure me nts , adjustme nts , illustrations , and othe r items can cha ng e at any time. These cha ng es can
affect the service tha t is given to the produc t. Ob tain the comp lete and mos t current informa tion before
you start any job. Pe rkins dealers or Pe rkins distributors ha ve the mos t current informa tion available.
When replacement parts are required for this
product Perkins recommends using Perkins
replacement parts.
Failure to heed this warning can lead to prema-
ture failures, product damage, personal injury or
death.
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
3
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
Atmospheric Pressure Sensor .............................. 46
Inlet Manifold Temperature Sensor ....................... 47
Temperature Sensor (DPF Inlet) ........................... 47
Pressure Sensor (NOx Reduction System) .......... 47
Temperature Sensor (NOx Reduction System) .... 48
Speed/Timing Sensor .......................................... 48
Electronic Control Module ..................................... 49
Glow Plugs ........................................................... 50
Air Compressor (Twin Cylinder Compressor) ....... 50
Air Compressor (Single Cylinder) ......................... 51
Specifications Section
Engine Design .....................................................
Fuel Injection Lines ..............................................
Fuel Injection Pump .............................................
Fuel Injectors .......................................................
Fuel Transfer Pump .............................................
Fuel Filter Base (Single Secondary Fuel Filter
Base) ...................................................................
Fuel Filter Base (Twin Secondary Fuel Filter
Base) ...................................................................
Fuel Filter Base (Primary Fuel Filter Base) ...........
Fuel Manifold (Rail) ...............................................
Lifter Group ...........................................................
Rocker Shaft ........................................................
4
4
5
6
6
Index Section
7
Index ..................................................................... 53
7
8
8
9
9
Valve Mechanism Cover ...................................... 10
Cylinder Head Valves ........................................... 11
Cylinder Head ...................................................... 12
Turbocharger ........................................................ 14
Exhaust Gas Valve (NRS) .................................... 15
Exhaust Sensor and Lines Gp (NRS) ................... 16
Exhaust Cooler (NRS) .......................................... 16
Exhaust Manifold ................................................. 19
Flexible Exhaust Pipe ........................................... 20
Diesel Particulate Filter ......................................... 20
Camshaft ............................................................. 21
Camshaft Bearings .............................................. 22
Engine Oil Filter Base .......................................... 22
Engine Oil Cooler ................................................. 23
Engine Oil Pump .................................................. 23
Engine Oil Pressure ............................................. 24
Engine Oil Pan ..................................................... 25
Crankcase Breather ............................................. 27
Water Temperature Regulator and Housing ......... 27
Water Pump ......................................................... 28
Cylinder Block ...................................................... 28
Crankshaft ........................................................... 29
Crankshaft Seals ................................................. 30
Vibration Damper and Pulley ............................... 31
Connecting Rod Bearing Journal ......................... 31
Main Bearing Journal ............................................ 32
Connecting Rod ................................................... 32
Piston and Rings .................................................. 34
Piston Cooling Jet ................................................. 35
Accessory Drive (SAE “B”) ................................... 35
Accessory Drive ................................................... 36
Front Housing and Covers ................................... 36
Gear Group (Front) ............................................... 37
Flywheel ............................................................... 38
Flywheel Housing ................................................ 39
Belt Tensioner ....................................................... 40
Refrigerant Compressor ....................................... 40
Fan Drive ............................................................. 41
Engine Lifting Bracket ........................................... 41
Alternator ............................................................. 41
Starter Motor ........................................................ 43
Coolant Temperature Sensor ............................... 45
Engine Oil Pressure Sensor ................................. 45
Boost Pressure Sensor ......................................... 46
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
4
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
Specifications Section
i04085729
Fuel Injection Lines
i03898012
Engine Design
Contact with high pressure fuel may cause fluid
penetration and burn hazards. High pressure fu-
el spray may cause a fire hazard. Failure to fol-
low these inspection, maintenance and service in-
structions may cause personal injury or death.
Refer to Operation and Maintenance Manual,
“General Hazard Information and High Pressure Fuel
Lines” before adjustments and repairs are performed.
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
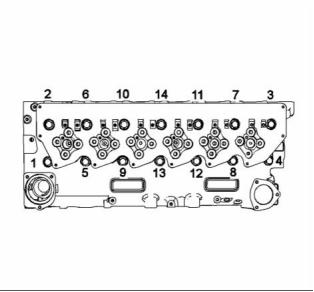
g01284058
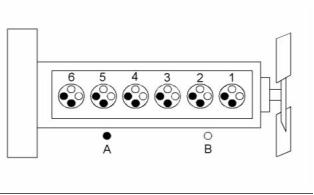
Illustration 1
Cylinder and valve location
(A) Exhaust valve
(B) Inlet valve
Ensure that all adjustments and repairs are performed
by authorized personnel that have had the correct
training.
Bore ......................................... 105 mm (4.133 inch)
Stroke ...................................... 127 mm (5.000 inch)
Displacement ..................... 6.6 L (402.76 cubic inch)
Cylinder arrangement ..................................... In-line
Type of combustion ............................ Direct injection
Compression ratio
Turbocharged charge cooled .................... 16.5:1
Number of cylinders ................................................ 6
Valves per cylinder .................................................. 4
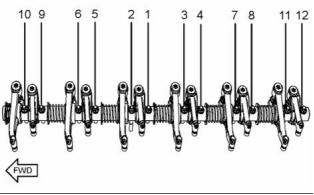
Firing order ......................................... 1, 5, 3, 6, 2, 4
When the crankshaft is viewed from the front of
the engine, the crankshaft rotates in the following
direction: ................................................... Clockwise
When the camshaft is viewed from the front of
the engine, the camshaft rotates in the following
direction: ................................................... Clockwise
The front of the engine is opposite the flywheel end.
The left side and the right side of the engine are
viewed from the flywheel end. The No. 1 cylinder is
the front cylinder.
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
5
Specifications Section
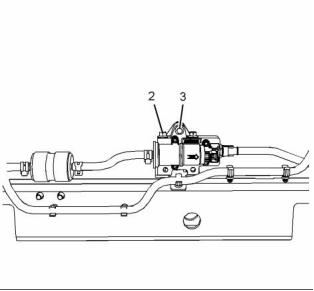
g02293673
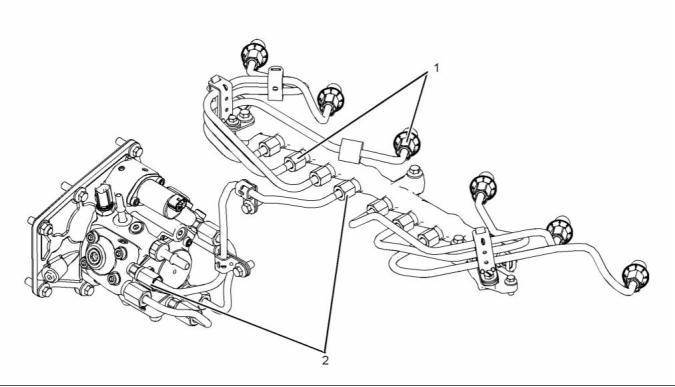
Illustration 2
Typical example
(1), (2) Tighten the nuts on the high-pressure fuel
lines to the following torque. ..... 40 N·m (30 lb ft)
i04085749
Fuel Injection Pump
Note: The timing of the fuel injection pump will need
to be checked by trained personnel. In order to check
the timing of the fuel injection pump, refer to Systems
Operation, Testing and Adjusting, “Fuel Injection
Pump Timing - Check”.
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
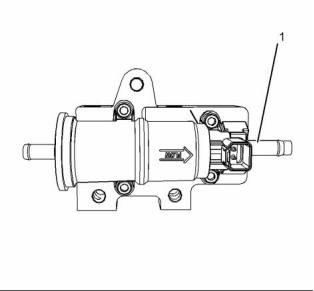
g02293713
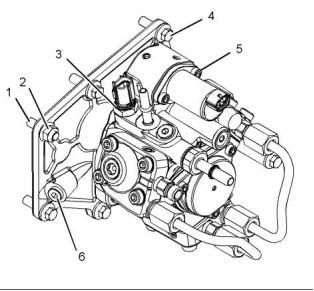
Illustration 3
Typical example
(1) Tighten the studs to the following torque. .. 11 N·m
(97 lb in)
(2) Tighten the mounting nut to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(3) Tighten the fuel temperature sensor to the
following torque. ....................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
6
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
(4) Tighten the setscrews to the following
i04083730
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
Fuel Transfer Pump
(5) Tighten the screws for the suction control valve
to the following torque. ............... 9 N·m (80 lb in)
(6) Tighten the screw to the following
torque. ...................................... 14 N·m (10 lb ft)
i03631793
Fuel Injectors
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
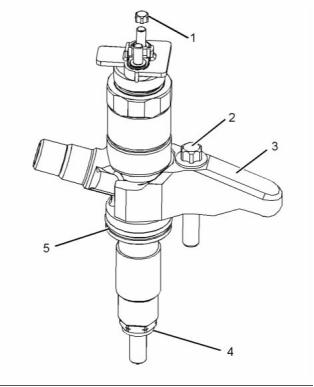
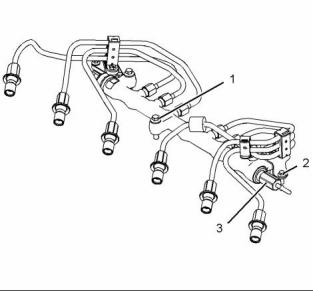
g02291814
Illustration 5
Typical example
(1) Tighten the connection to the following
torque. ...................................... 20 N·m (15 lb ft)
g01862457
Illustration 4
Typical example
(3) Clamp
(4) Washer
(5) O ring seal
g02291815
Illustration 6
Typical example
(2), (3) Tighten the bolts to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(1) Torque for the nuts ...................... 2 N·m (18 lb in)
(2) Torque for the bolt in the clamp for the fuel
injection nozzle ...................... 21 N·m (15.5 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
7
Specifications Section
i04364060
i04364061
Fuel Filter Base
(Single Secondary Fuel Filter
Base)
Fuel Filter Base
(Twin Secondary Fuel Filter
Base)
NOTICE
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
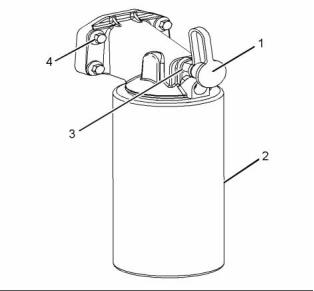
If necessary, install a new fuel filter (2) to canister (1).
Refer to Operation and Maintenance Manual, “Fuel
System Secondary Filter - Replace” for the correct
procedure.
If necessary, install a new fuel filter (2) to canister (1).
Refer to Operation and Maintenance Manual, “Fuel
System Secondary Filter - Replace” for the correct
procedure.
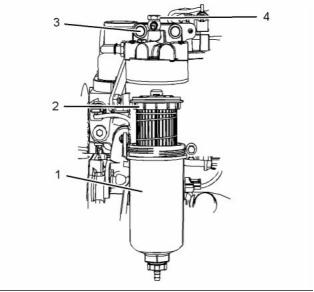
g02516539
Illustration 7
Typical example
(3) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 44 N·m
(33 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 17 N·m
(13 lb ft)
g02518537
Illustration 8
Typical example
(3) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 44 N·m
(33 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 17 N·m
(13 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
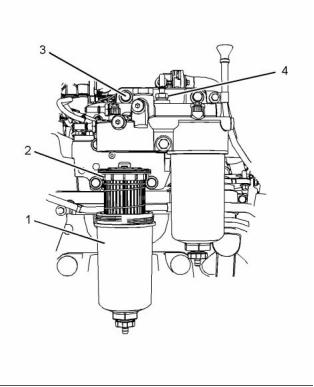
8
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
i04363635
i04084390
Fuel Filter Base
Fuel Manifold (Rail)
(Primary Fuel Filter Base)
Refer to Operation and Maintenance Manual,
“General Hazard Information and High Pressure Fuel
Lines” before adjustments and repairs are performed.
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
NOTICE
Refer to Systems Operation, Testing and Adjust-
ing, “Cleanliness of Fuel System Components” for
detailed information on the standards of cleanli-
ness that must be observed during ALL work on
the fuel system.
If necessary, install a new fuel filter element to
canister (2). Refer to Operation and Maintenance
Manual, “Fuel System Primary Filter (Water
Separator) Element - Replace” for the correct
procedure.
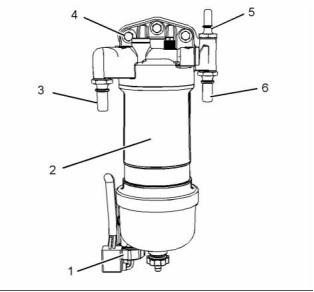
g02293653
Illustration 10
Typical example
g02289936
(1) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
Illustration 9
Typical example
(2) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 10 N·m
(89 lb in)
Tighten water in fuel switch (1) hand tight.
(3) Tighten the connection to the following
torque. ...................................... 17 N·m (13 lb ft)
(3) Tighten the fuel pressure relief valve to the
following torque. ....................... 30 N·m (22 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 44 N·m
(32 lb ft)
Note: The fuel pressure relief valve (3) should be
tightened an additional 24 degrees.
(5) Tighten the connection to the following
torque. ...................................... 17 N·m (13 lb ft)
(6) Tighten the connection to the following
torque. ...................................... 17 N·m (13 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
9
Specifications Section
i03537811
i03519944
Lifter Group
Rocker Shaft
g01866794
Illustration 11
Typical example
(A) Diameter of the lifter body .. 21.938 to 21.963 mm
(0.86370 to 0.86468 inch)
Bore diameter in the cylinder block
...... 22.000 to 22.032 mm (0.86614 to 0.86740 inch)
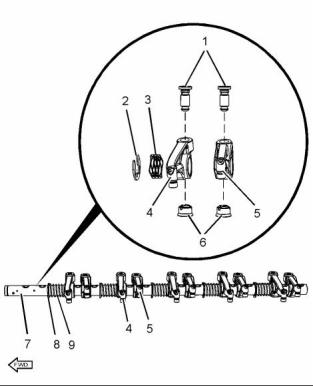
g02113434
Illustration 12
Typical example
Clearance
(1) Tighten the threaded inserts to the following
torque. ...................................... 30 N·m (22 lb ft)
Clearance of the lifter .......... 0.037 to 0.094 mm
(0.00146 to 0.00370 inch)
(2) Retaining clip
(3) Spring
(4) Inlet rocker arm
Diameter of the rocker arm bore
.... 25.013 to 25.051 mm (0.9848 to 0.9863 inch)
(5) Exhaust rocker arm
Diameter of the rocker arm bore
.... 25.013 to 25.051 mm (0.9848 to 0.9863 inch)
Clearance
Maximum clearance of both the rocker arm
bores. ............................ 0.089 mm (0.0035 inch)
The service limit for both rocker arm
bores ............................... 0.17 mm (0.0067 inch)
(6) Guide
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()

![]()
10
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
(7) Rocker shaft
Diameter of the rocker
shaft .................................. 24.962 to 24.987 mm
(0.98275 to 0.98374 inch)
(8) Retaining clip
(9) Spring
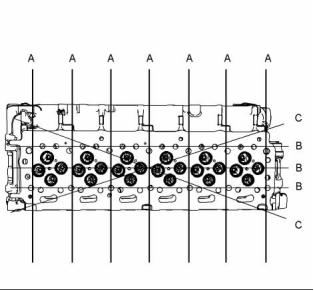
g01850497
Illustration 13
Tightening sequence
Tighten the fasteners in the sequence that is in
illustration 13. Tighten the fasteners to the following
torque. ............................................. 35 N·m (26 lb ft)
i03532881
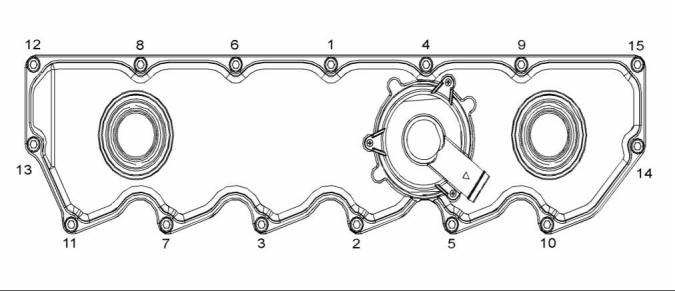
Valve Mechanism Cover
g01861234
Illustration 14
Typical example
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
11
Specifications Section
Tighten the bolts for the valve mechanism cover in
the sequence that is shown in illustration 14. Torque
for the bolts ....................................... 9 N·m (80 lb in)
Table 2
The load for the exhaust
valve spring
The length of the exhaust
valve spring
285 to 315 N
31.5 mm (1.2402 inch)
i03538600
(64.07085 to 70.81515 lb)
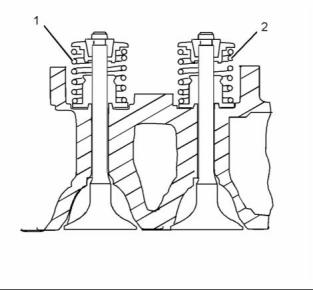
Cylinder Head Valves
408.5 to 451.5 N
(91.83488 to 101.50172 lb)
22.3 mm (0.87795 inch)
Note: The free length for the exhaust valve spring is
52.73 mm (2.07598 inch).
g01927357
Illustration 16
Typical example
(3) Valve face angle
Inlet ................................................... 30 degrees
Exhaust ............................................. 45 degrees
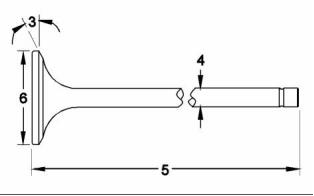
g01927355
Illustration 15
Typical example
(4) Valve stem diameter
(1) Exhaust valve spring
(2) Inlet valve spring
Inlet .. 6.970 to 6.985 mm (0.2744 to 0.2750 inch)
Exhaust ................................. 6.945 to 6.960 mm
(0.2734 to 0.2740 inch)
When the valve springs are replaced the valve
springs must be replaced in pairs.
Clearance
Refer to table 1 and table 2 for information on the
length of the valve spring and the load of the valve
spring.
Maximum clearance of the inlet valve
stem ................................ 0.05 mm (0.0020 inch)
The service limit for the inlet valve
Table 1
stem ................................ 0.08 mm (0.0031 inch)
The load for the inlet valve The length of the inlet valve
spring
spring
Clearance
161.5 to 178.5 N
(36.30682 to 40.12859 lb)
31.5 mm (1.2402 inch)
Maximum clearance of the exhaust valve
stem ............................ 0.075 mm (0.00295 inch)
The service limit for the exhaust valve
337.9 to 373.5 N
(75.96330 to 83.96654 lb)
21.5 mm (0.84646 inch)
stem .............................. 0.10 mm (0.00394 inch)
(5) Length of valve
Note: The free length for the inlet valve spring is
40.65 mm (1.60039 inch).
Inlet valve .......................... 109.82 to 110.27 mm
(4.32361 to 4.34133 inch)
Exhaust valve ................ 109.853 to 110.303 mm
(4.32491 to 4.34263 inch)
(6) Valve head
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()


![]()
12
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
Diameter of inlet valve head .................... 35 mm
(1.37795 inch)
Diameter of exhaust valve head .............. 33 mm
(1.2992 inch)
i04314230
Cylinder Head
g01854993
Illustration 18
Typical example
Note: The maximum distortion of the cylinder head
is given in table 3.
Table 3
Maximum Permissible
Dimension
Distortion
Width (A)
Length (B)
0.03 mm (0.0012 inch)
0.05 mm (0.0020 inch)
0.05 mm (0.020 inch)
g01852017
Illustration 17
Diagonal Line (C)
Typical example
Lubricate the threads and the underside of the head
bolts with clean engine oil.
Tighten the bolts in the sequence that is shown in
illustration 17. Torque for the bolts ........... 50 N·m
(37 lb ft)
Tighten the bolts again to the following
torque. .................................... 100 N·m (74 lb ft)
Tighten the head bolts to the additional
amount. ........................................... 225 degrees
Minimum thickness of cylinder head ......... 150.8 mm
(5.93700 inch)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()

KENR9113-01
13
Specifications Section
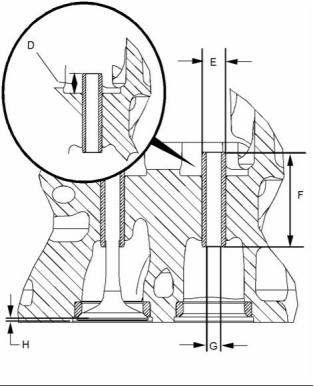
g02328933
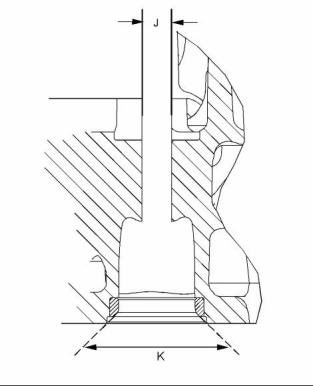
g02474819
Illustration 19
Illustration 20
Typical example
Typical example
(D) Valve guide height from the top of the valve guide
to the valve spring seat .......... 10.75 to 11.25 mm
(0.42323 to 0.44291 inch)
(J) Diameter of the parent bore in the cylinder
head ................................... 11.000 to 11.022 mm
(0.43307 to 0.43394 inch)
(E) Outside diameter of the valve
guides ................................ 11.029 to 11.040 mm
(0.43421 to 0.43464 inch)
(K) Seat angle
Inlet ............................................. 119.15 degrees
Exhaust ........................................ 89.15 degrees
(F) Length of the valve guides ... 43.75 to 44.25 mm
(1.72244 to 1.74212 inch)
(G) Internal diameter of the valve
guides ................................... 7.007 to 7.020 mm
(0.27587 to 0.27638 inch)
(H) Valve depths
Inlet .. 0.905 to 1.163 mm (0.0356 to 0.0458 inch)
The service limit for the depth of the inlet valve
........................................ 1.41 mm (0.0555 inch)
Exhaust ................................. 0.876 to 1.131 mm
(0.0345 to 0.0445 inch)
The service limit for the exhaust valve
depth ............................... 1.38 mm (0.0543 inch)
g02475018
Illustration 21
Typical example
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
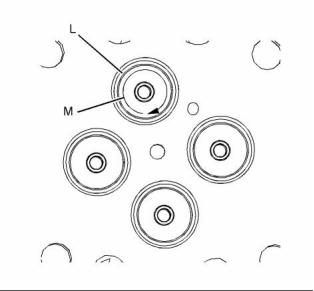
14
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
(L) Seat surface finish ...................... Ra 0.8 microns
The test pressure for the wastegate
actuator ........................................ 100 kPa (14.5 psi)
(M) Concentricity of valve seat to valve guide
parent bore Maximum Total Indicated Reading
(TIR) ............................. 0.08 mm (0.00315 inch)
The movement for the rod actuator ................. 1 mm
(0.0394 inch)
i04136811
Turbocharger
g02334338
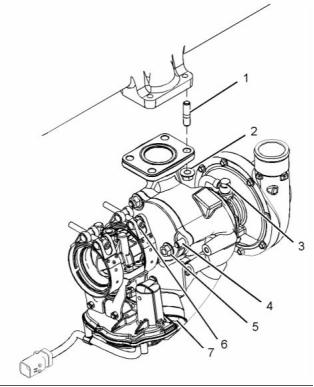
Illustration 23
Typical example
(8) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. ... 9 N·m
(80 lb in)
(9) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 33 N·m
(24 lb ft)
(10) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. .. 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
g02334286
Illustration 22
Typical example
(1) Tighten the studs to the following
torque. ...................................... 18 N·m (13 lb ft)
(2) Tighten the nuts to the following torque. .. 44 N·m
(32 lb ft)
(3) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 15 N·m
(11 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the studs to the following
torque. ...................................... 18 N·m (13 lb ft)
(5) Tighten the nuts to the following torque. .. 44 N·m
(32 lb ft)
(6) Tighten the band clamps to the following
torque. .................................... 12 N·m (106 lb in)
(7) Actuator
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
15
Specifications Section
i04087589
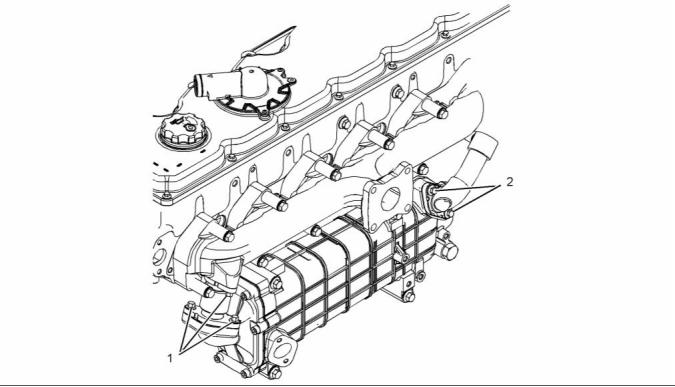
Exhaust Gas Valve (NRS)
g01946893
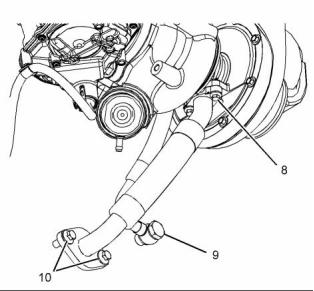
Illustration 24
Typical example
(1) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
g02295533
Illustration 25
Typical example
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
16
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
(2) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 18 N·m
(13 lb ft)
(3) Tighten the bolts to the following torque. .. 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the clamps to the following
torque. ........................................ 7 N·m (62 lb in)
(5) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 18 N·m
(13 lb ft)
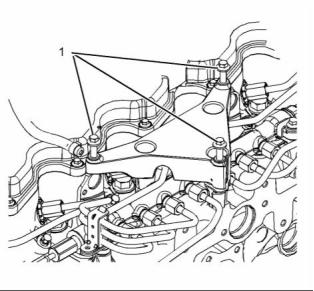
g02148954
Illustration 27
Typical example
Note: Apply Tooling (A) to the sensors before the
sensors are installed.
(1) Tighten the sensors to the following
torque. ...................................... 45 N·m (33 lb ft)
Tighten the harness for the sensors (not shown) to
the following torque. .................... 1.2 N·m (10.6 lb in)
g02295655
Illustration 26
Typical example
i04087771
Exhaust Cooler (NRS)
(6) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 15 N·m
(11 lb ft)
(7), (8) Tighten the fasteners to the following
torque. ...................................... 18 N·m (13 lb ft)
Note: When the pipes for the exhaust cooler are
removed or installed, care must be taken so that the
pipes are not bent or damaged.
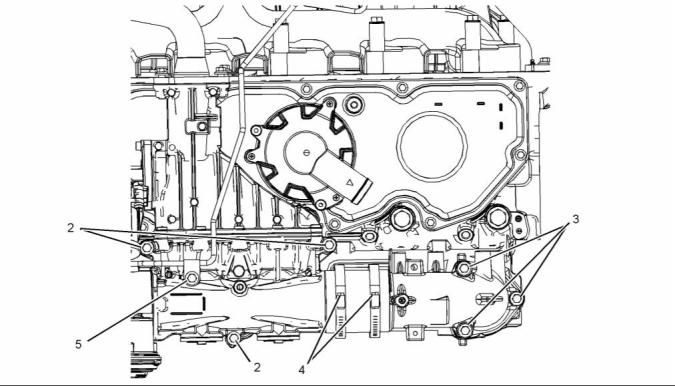
i04364929
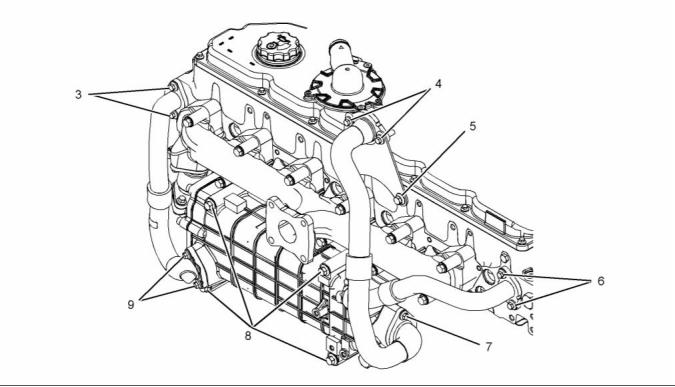
Exhaust Sensor and Lines Gp
(NRS)
Table 4
Required Tools
Tool
Part Number
Part Description
QTY
Bostik Pure Nickel
Anti-Seize Compound
A
-
1
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()

![]()
KENR9113-01
17
Specifications Section
g02295833
Illustration 28
Typical example
(1) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(2) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 18 N·m (13 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
18
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
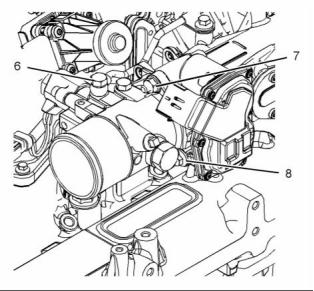
g02295755
Illustration 29
Typical example
(3), (6) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(4), (7), (9) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 18 N·m (13 lb ft)
(5), (8) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 44 N·m (32 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
19
Specifications Section
i04364975
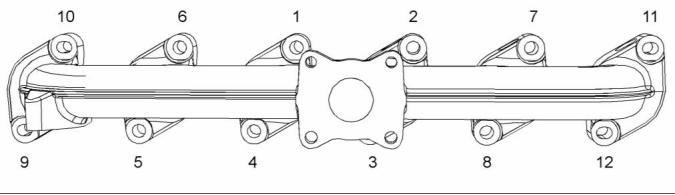
Exhaust Manifold
g02330776
Illustration 30
Typical example
Tighten the exhaust manifold bolts in the sequence
that is shown in illustration 30 to the following
torque. ............................................. 44 N·m (32 lb ft)
To measure the flatness of the exhaust manifold,
follow step 1 to step 4.
1. Remove all bolts and spacers from the exhaust
manifold.
2. Install two spacers and bolts into holes eleven and
twelve of port one of the exhaust manifold.
3. Tighten the bolts to a torque of 44 N·m (32 lb ft).
4. Use a suitable feeler gauge to measure the gap
that is between port six (holes nine and ten) of the
exhaust manifold and the cylinder head.
The maximum amount that the gap should be
is ........................................... 1.4 mm (0.05512 inch)
For the correct procedures to remove and install
the exhaust manifold, refer to Disassembly and
Assembly.
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
20
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
i03936932
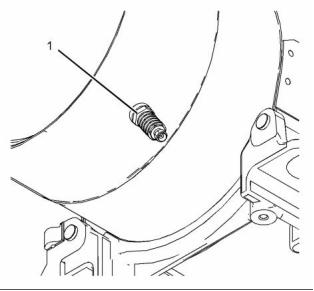
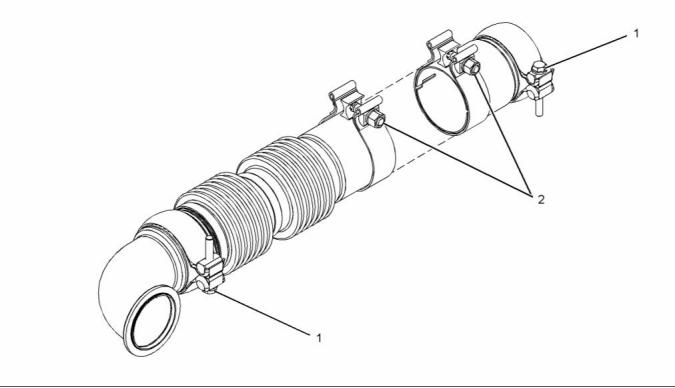
Flexible Exhaust Pipe
g02155429
Illustration 31
Typical example
(1) Tighten the clamp to the following
torque. ...................................... 35 N·m (26 lb ft)
(2) Tighten the clamp to the following
torque. ...................................... 55 N·m (41 lb ft)
Refer to Disassembly and Assembly for the correct
procedure to install the flexible exhaust pipe.
i04229372
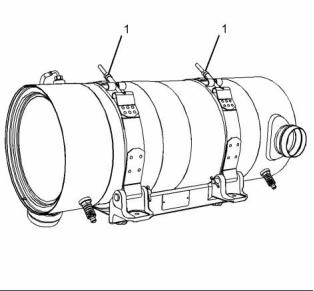
Diesel Particulate Filter
Note: To remove and install the Diesel Particulate
Filter (DPF), refer to Disassembly and Assembly for
the correct procedures.
g02405938
Illustration 32
Typical example
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
21
Specifications Section
(1) Tighten the nuts on clamps to the following
torque. ...................................... 17 N·m (13 lb ft)
(2) Bolt
Torque for the 8.8 graded bolt .. 95 N·m (70 lb ft)
Torque for the 10.9 graded bolt ............. 120 N·m
(89 lb ft)
i04314156
Camshaft
(3) The diameters of the camshaft journals are given
in the following tables.
Table 5
Camshaft Journals
from the Front End
of the Engine
Standard Diameter
1
Front
50.711 to 50.737 mm
(1.9965 to 1.9975 inch)
50.457 to 50.483 mm
(1.9865 to 1.9875 inch)
2
3
50.203 to 50.229 mm
(1.9765 to 1.9775 inch)
4
Rear
49.949 to 49.975 mm
(1.9665 to 1.9675 inch)
Maximum wear on the camshaft journals ... 0.05 mm
(0.0021 inch)
Check the camshaft lobes for visible damage. If a
new camshaft is installed, you must install new lifters.
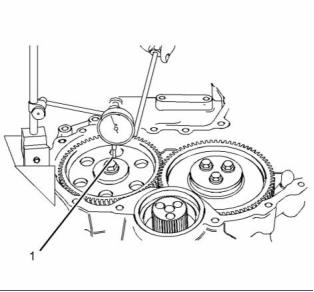
g01927854
Illustration 33
Checking the end play of the camshaft
(1) End play of a camshaft ......... 0.106 to 0.558 mm
(0.00417 to 0.02197 inch)
Maximum permissible end play of a worn
camshaft ............................... 0.62 mm (0.0244 inch)
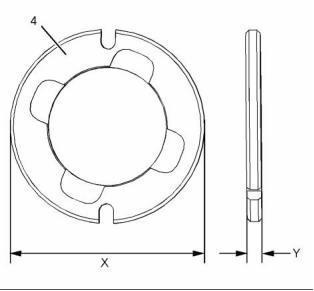
g02474757
Illustration 35
Typical example
(4) Camshaft thrust washer
Outer diameter (X) ............ 72.949 to 73.000 mm
(2.872 to 2.874 inch)
Thickness (Y) ........................ 5.486 to 5.537 mm
(0.21598 to 0.21799 inch)
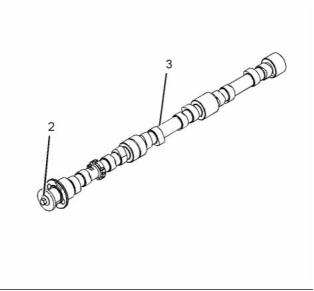
g01859007
Illustration 34
Typical example
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
22
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
i03530782
i03551117
Camshaft Bearings
Engine Oil Filter Base
g01859293
g01877935
Illustration 36
Illustration 37
Typical example
Typical example
(1) The diameter of the installed camshaft
(1) Dust cap
bearing .............................. 50.787 to 50.848 mm
(1.9995 to 2.0019 inch)
(2) Engine oil filter
Torque for the engine oil filter .. 12 N·m (106 lb in)
(3) Engine oil sampling valve
Torque for the engine oil sampling valve (if
equipped) ................................ 12 N·m (106 lb in)
Torque for the plug (if equipped) ... 12 N·m (106 lb in)
(4) Setscrew
Torque for the setscrews that retain the oil filter
base .......................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()

![]()
KENR9113-01
23
Specifications Section
i03524541
Tighten the setscrews in the sequence that is in
illustration 39 to the following torque. ...... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
Engine Oil Cooler
i04363634
Engine Oil Pump
Engine Oil Cooler with a Low
Mounted Filter Base
Type ............................. Gear-driven differential rotor
Number of lobes
Inner rotor ......................................................... 6
Outer rotor ........................................................ 7
g02005253
Illustration 38
Typical example
Setscrews
Tighten the setscrews in the sequence that is in
illustration 38 to the following torque. ...... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
g00938064
Illustration 40
Engine Oil Cooler with a High
Mounted Filter Base
(1) Clearance of the outer rotor to the
body ...................................... 0.050 to 0.330 mm
(0.0020 to 0.0130 inch)
g00938061
Illustration 41
Checking the clearance
(2) Service limit of inner rotor to outer
rotor ...................................... 0.080 to 0.250 mm
(0.0031 to 0.0098 inch)
g01854213
Illustration 39
Typical example
Setscrews
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
<, P>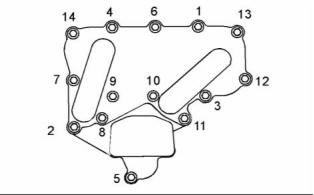

24
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
i03540441
Engine Oil Pressure
The minimum oil pressure at a maximum engine
speed of 2200 rpm and at normal operating
temperature is the following value. .. 315 kPa (45 psi)
g00938799
Illustration 42
Checking the end play
(3) End play of rotor assembly
Inner rotor ............................. 0.050 to 0.180 mm
(0.0020 to 0.0071 inch)
Outer rotor ............................ 0.050 to 0.180 mm
(0.0020 to 0.0071 inch)
g02293754
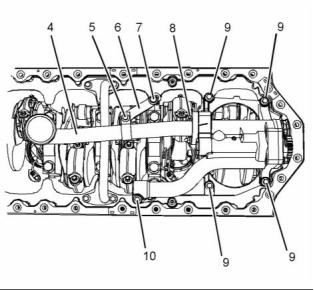
Illustration 43
Typical example
(4) Suction Pipe
(6) Bracket for the Suction Pipe
(5), (8), (9), (10) Tighten the bolts to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(7) Tighten the bolt to the following torque. ... 44 N·m
(32 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
25
Specifications Section
i04129089
Engine Oil Pan
g01856874
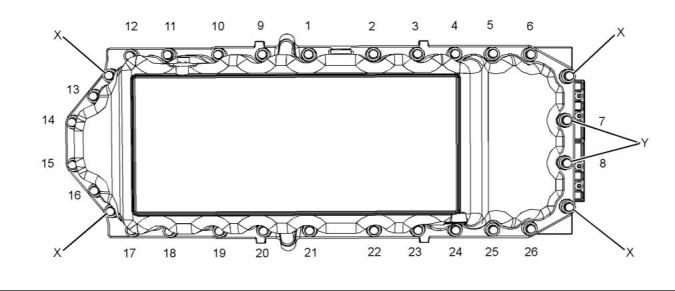
Illustration 44
(X) Guide studs
(Y) Short fastener
Tighten the fasteners in the sequence that is shown
in illustration 44. Torque for the fasteners ...... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
g01857014
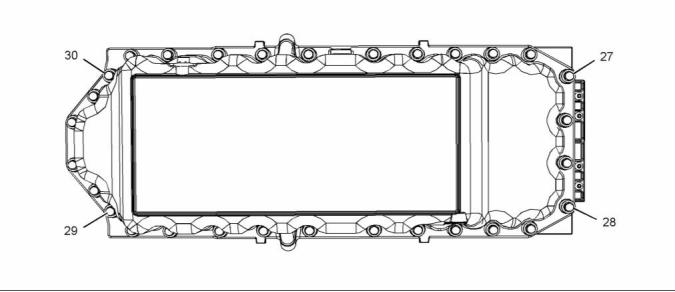
Illustration 45
Remove the guide studs. Install the fasteners (27),
(28), (29) and (30).
Tighten the oil drain plug to the following
torque. ............................................. 34 N·m (25 lb ft)
Tighten the fastener in the sequence that is shown in
illustration 45. Torque for the fasteners .......... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
Tighten the oil level switch (if equipped) to the
following torque. .............................. 34 N·m (25 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
26
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
Refer to the Disassembly and Assembly, “Engine Oil
Pan” for the correct procedure to install the engine
oil pan.
The Cast Iron Oil Pan
g01397669
Illustration 46
Tightening sequence
Tighten the fasteners in the sequence that is shown
in illustration 46 to the following torque. ......... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
Tighten the oil drain plug to the following
torque. ............................................. 34 N·m (25 lb ft)
Tighten the oil level switch (if equipped) to the
following torque. .............................. 34 N·m (25 lb ft)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
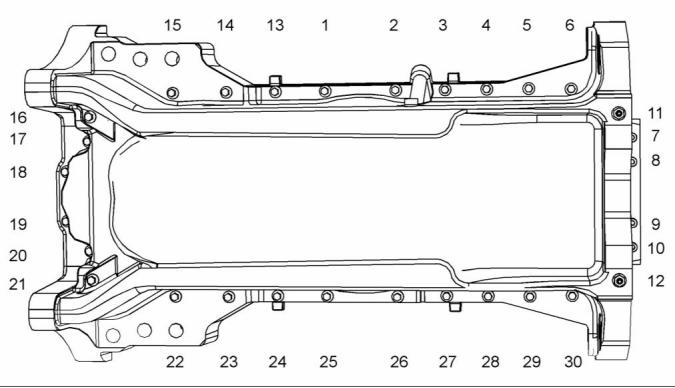
KENR9113-01
27
Specifications Section
i04085789
i03520180
Water Temperature Regulator
and Housing
Crankcase Breather
g01853873
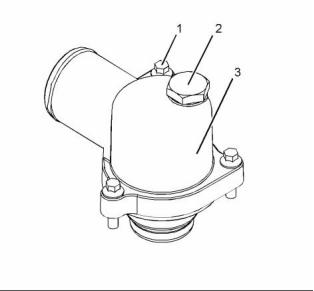
Illustration 48
Typical example
Water temperature regulator housing
(1) Torque for the bolts that fasten the housing to the
cylinder head ............................ 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
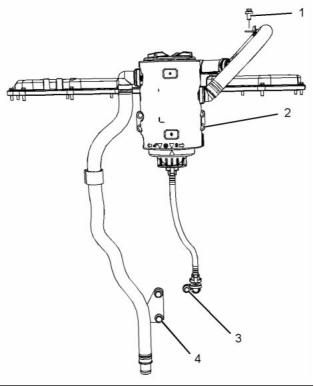
g02295333
Illustration 47
Typical example
(2) Torque for the vent plug ....... 22 N·m (16.22 lb ft)
(1), (2), (3) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
(4) Tighten the setscrews to the following
torque. ...................................... 44 N·m (32 lb ft)
Note: If a hexagonal pillar spacer is required, install
the spacer to the engine oil cooler. Tighten the spacer
to a torque of 22 N·m (16 lb ft).
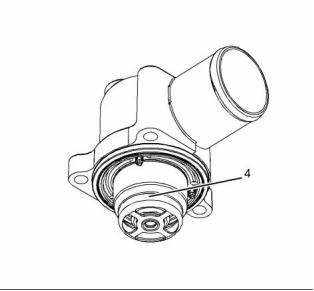
g01854133
Illustration 49
(4) Water temperature regulator
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
28
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
Opening temperature ........................ 80° to 84°C
(151° to 176°F)
Maximum open length of 11 mm (0.43307 inch) is
achieved at the following temperature. ...... 94° C
(201° F)
i04117792
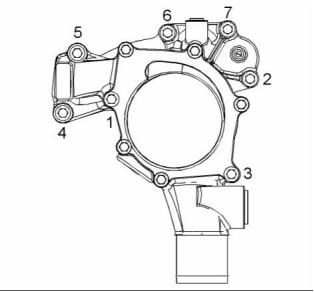
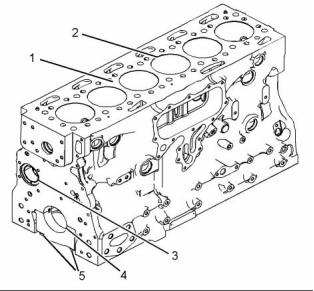
Cylinder Block
i03899331
Water Pump
g01855114
Illustration 51
Cylinder block
(1) Cylinder block
(2) Cylinder bore ................ 105.000 to 105.025 mm
(4.1338 to 4.1348 inch)
g02142711
Illustration 50
Tightening sequence
(3) Camshaft bearings
Tighten the setscrews in the numerical sequence
that is shown in illustration 50 to the following
torque. ............................................. 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
Diameter of the bushing in the cylinder
block for the number 1 camshaft
bearing .............................. 55.563 to 55.593 mm
(2.1875 to 2.1887 inch)
Diameter of the bore in the cylinder
block for the number 2 camshaft
journal ............................... 50.546 to 50.597 mm
(1.9900 to 1.9920 inch)
Diameter of the bore in the cylinder
block for the number 3 camshaft
journal ............................... 50.292 to 50.343 mm
(1.9800 to 1.9820 inch)
Diameter of the bore in the cylinder
block for the number 4 camshaft
journal ............................... 50.038 to 50.089 mm
(1.9700 to 1.9720 inch)
(4) Main bearings
Bore in the cylinder block for the main
bearings ............................ 88.246 to 88.272 mm
(3.4742 to 3.4753 inch)
(5) Main bearing cap bolts
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
KENR9113-01
29
Specifications Section
Use the following procedure in order to install the
main bearing cap bolts:
Standard thickness of thrust
washer ...... 2.69 to 2.75 mm (0.1059 to 0.1083 inch)
1. Apply clean engine oil to the threads of the main
bearing cap bolts.
Oversize thickness of thrust
washer ....... 2.89 to 2.95 mm (0.1138 to 0.1161 inch)
2. Put the main bearing caps in the correct position
that is indicated by a number on the top of the
main bearing cap. Install the main bearing caps
with the locating tabs in correct alignment with the
recess in the cylinder block.
3. Evenly tighten the main bearing cap bolts.
Torque for the main bearing cap bolts. ...... 80 N·m
(59 lb ft)
4. After torquing the bolts for the main bearing caps,
the bolts must be rotated for an additional 90
degrees.
Note: Ensure that the crankshaft can rotate freely.
i04029133
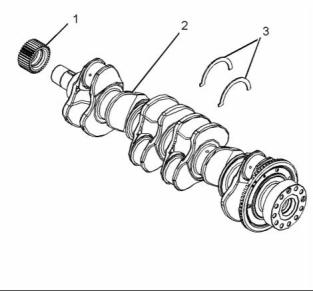
Crankshaft
g01862538
Illustration 52
Typical example
(1) Crankshaft gear
(2) Crankshaft
(3) Crankshaft thrust washers
Maximum permissible temperature of the gear for
installation on the crankshaft ........... 180 °C (356 °F)
The end play of a new crankshaft ..... 0.1 to 0.41 mm
(0.00394 to 0.01614 inch)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
30
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
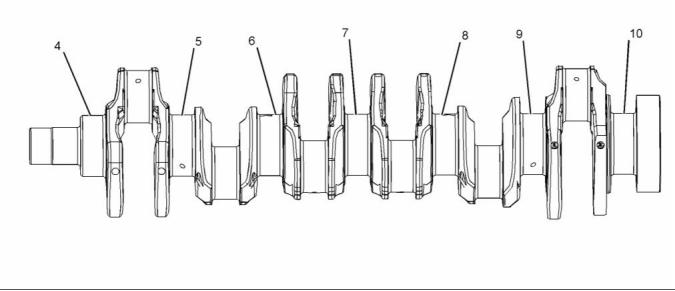
g01869273
i03520221
Illustration 53
(4) Journal 1
(5) Journal 2
(6) Journal 3
(7) Journal 4
(8) Journal 5
(9) Journal 6
(10) Journal 7
Refer to Table 6 for the run out of the crankshaft
journals.
Crankshaft Seals
Table 6
Journal
(1)
Run Out of the Journals
Mounting
(2)
0.05 mm (0.0020 inch)
0.1 mm (0.0039 inch)
0.15 mm (0.0059 inch)
0.1 mm (0.0039 inch)
0.05 mm (0.0020 inch)
Mounting
You do not need to remove the engine oil pan in
order to install the oil seal.
(3)
(4)
Note: Some engines also have an oil seal that
is installed in the flywheel housing. Refer to
Specifications, “Flywheel Housing” for more
information.
(5)
(6)
(7)
Inspect the crankshaft for wear or for damage. For
more information regarding the servicing of the
crankshaft, contact the Global Technical Support
Center.
Refer to Specifications, “Connecting Rod Bearing
Journal” for more information on the connecting rod
bearing journals and connecting rod bearings.
Refer to Specifications, “Main Bearing Journal” for
information on the main bearing journals and for
information on the main bearings.
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
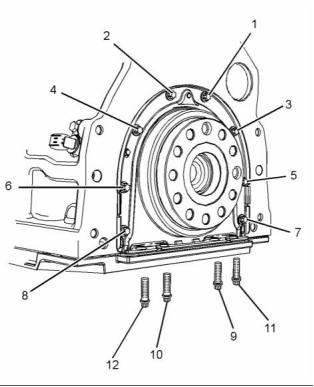
KENR9113-01
31
Specifications Section
The sequence for installation of the
rear oil seal
i03930112
Vibration Damper and Pulley
g02153930
Illustration 55
Typical example
g01863635
Illustration 54
(1) Tighten the setscrews for the adapter to the
following torque. ....................... 40 N·m (30 lb ft)
Typical example
(11), (12) Torque for the fasteners .. 15 N·m (11 lb ft)
(1), (2) Torque for the fastener ...... 22 N·m (16 lb ft)
Loosen fastener (11) and (12) by one complete turn.
The setscrews (1) must be tightened through an
angle of 120 degrees.
(2) Tighten the bolts for the damper and pulley to the
following torque. ...................... 115 N·m (85 lb ft)
Tighten the fasteners in the sequence that is in
illustration 54. Torque for the fasteners .......... 22 N·m
(16 lb ft)
(3) Vibration damper
(4) Crankshaft pulley
(5) Crankshaft adapter
The maximum out of concentricity between the
crankshaft flange and the outside diameter of the
rear seal for the crankshaft. .. 0.4 mm (0.01575 inch)
i04067349
Connecting Rod Bearing
Journal
The original size of the connecting rod bearing journal
on the crankshaft .................... 71.970 to 71.990 mm
(2.83346 to 2.83425 inch)
Maximum permissible wear of a bearing journal
on the crankshaft when a new connecting rod is
installed ................................. 0.04 mm (0.0016 inch)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()
![]()
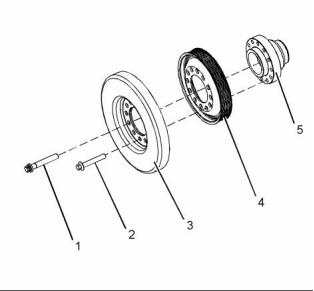
32
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
Width of the connecting rod bearing journals on the
crankshaft ............................... 37.962 to 38.038 mm
(1.4946 to 1.4976 inch)
Thickness at center of the shells of oversize bearing
shell 0.76 mm (0.030 inch) ......... 2.480 to 2.486 mm
(0.09764 to 0.09787 inch)
Radius of the fillet of the connecting rod bearing
journals ......... 3.68 to 3.96 mm (0.145 to 0.156 inch)
Width of the main bearing shells .. 26.32 to 26.58 mm
(1.03622 to 1.04645 inch)
Surface finish of connecting rod bearing
journals ............................................. Ra 0.2 microns
Clearance between the bearing shell and the main
bearing journals .......................... 0.036 to 0.094 mm
(0.00142 to 0.00370 inch)
Surface finish of radii ........................ Ra 0.4 microns
i04234795
i04067350
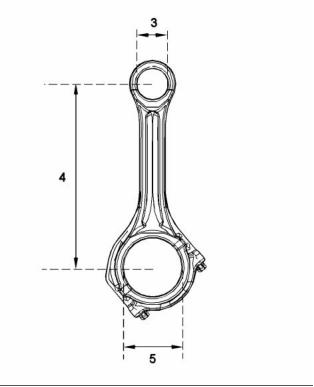
Connecting Rod
Main Bearing Journal
The original size of the main bearing
journal ..................................... 83.980 to 84.000 mm
(3.30629 to 3.30708 inch)
Maximum permissible wear of the main bearing
journals ............................... 0.040 mm (0.0016 inch)
Radius of the fillet of the main bearing
journals ....................................... 3.875 to 4.125 mm
(0.15256 to 0.16240 inch)
Surface finish of bearing journals and crank pins
.......................................................... Ra 0.2 microns
Surface finish of radii ........................ Ra 0.4 microns
Width of new main bearing journal where the thrust
washer is installed .................. 35.235 to 35.165 mm
(1.3872 to 1.3844 inch)
g01860862
Illustration 56
Width of new main bearing journal where the thrust
washer is not installed ................ 35.25 to 35.15 mm
(1.38779 to 1.38386 inch)
Typical example
(1) The bearing shell for the connecting rod
The shell for the main bearings
For the correct procedure to install the bearing
shell for the connecting rod, refer to Disassembly
and Assembly, “Pistons and Connecting Rods -
Assemble”.
The shells for the main bearings are available
for remachined journals which have the following
oversize dimensions.
Table 7
Oversize bearing shell ...... 0.25 mm (0.010 inch)
Oversize bearing shell ...... 0.50 mm (0.020 inch)
Oversize bearing shell ...... 0.76 mm (0.030 inch)
Thickness of Connecting
1.994 to 2.000 mm
Rod Bearing at the
(0.0785 to 0.0787 inch)
Center
Thickness at center of the shells of oversize bearing
shell 0.25 mm (0.010 inch) ......... 2.226 to 2.232 mm
(0.08764 to 0.08787 inch)
Thickness of Bearing
Cap at the Center
1.994 to 2.000 mm
(0.0785 to 0.0787 inch)
0.080 to 0.035 mm
(0.00315 to 0.00138 inch)
Bearing Clearance
Thickness at center of the shells of oversize bearing
shell 0.50 mm (0.020 inch) ......... 2.353 to 2.359 mm
(0.09264 to 0.09287 inch)
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()
![]()


KENR9113-01
33
Specifications Section
Table 8
Oversize Connecting Rod Bearing
0.25 mm (0.010 inch)
0.51 mm (0.020 inch)
0.76 mm (0.030 inch)
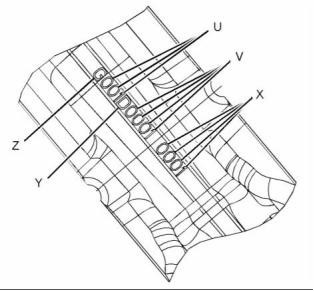
g01860878
Illustration 58
g01950657
Illustration 57
Typical example
(U) Day code
(V) Code for the connecting rod
(X) Code for the Connecting rod cap
(Y) Year code
Typical example
(3) Diameter of the finished bore for the piston
pin ..................................... 39.738 to 39.723 mm
(1.5645 to 1.5639 inch)
(Z) Code for the grade of connecting rod
(4) Distance between the parent bores
...... 219.05 to 219.1 mm (8.6240 to 8.6260 inch)
Note: The day code is from the first day in the
year. For example, “001” will be the first day of the
appropriate year.
(5) Diameter for the finished bore for the connecting
rod bearing ....................... 76.025 to 76.038 mm
(2.99310 to 2.99362 inch)
The mating surfaces of the connecting rod are
produced by hydraulically fracturing the forged
connecting rod. Ensure that the correct cap for
the connecting rod is installed with the correct
connecting rod. Ensure that the serial numbers for
both components match.
The connecting rod is color coded. The color code
is a reference for the length of the connecting rod.
Refer to table 9 for the length of connecting rod.
Table 9
Specifications for the Connecting Rod
(2) Torque of the setscrews for the connecting rod
.................................................. 40 N·m (30 lb ft)
Grade
Letter
Length Of The
Connecting Rod
Color Code
Tighten the setscrews for the connecting rod for
an additional 120 degrees. The setscrews for the
connecting rod (2) must be replaced after this
procedure.
161.107 to 161.140 mm
(6.3428 to 6.3441 inch)
B
Blue
Note: Always tighten the connecting rod cap to the
connecting rod, when the assembly is out of the
engine. Tighten the assembly to the following torque
20 N·m (14 lb ft).
This document is printed from SPI². Not for RESALE
![]()

![]()
![]()

34
KENR9113-01
Specifications Section
i04041471
Width of oil control ring ............. 2.97 to 2.99 mm
(0.1169 to 0.1177 inch)
Piston and Rings
The clearance between a new oil control ring and
the groove in a new piston ........ 0.03 to 0.07 mm
(0.0011 to 0.0027 inch)
Ring gap ................................... 0.30 to 0.55 mm
(0.0118 to 0.0216 inch)
Note: When you install a new oil control ring, make
sure that the word “TOP” is facing the top of the
piston. New oil control rings have a red identification
mark. The identification mark must be on the left
of the ring end gap when the top piston ring is
installed on an upright piston. The oil control ring is
a two-piece ring that is spring loaded. A pin is used
in order to hold both ends of the spring of the oil
control ring in position. The ends of the spring of the
oil control ring must be installed opposite the end gap
of the oil control ring.
Note: Ensure that the ring end gaps of the piston
rings are spaced 120 degrees from each other.
g01155119
Illustration 59
Typical example
Piston
(1) Top compression ring
The shape of the top compression
ring ....................................................... Keystone
Note: An arrow which is marked on the piston crown
must be toward the front of the engine.
Ring gap ................................... 0.30 to 0.40 mm
(0.01181 to 0.01575 inch)
Piston height above cylinder block .. 0.55 to 0.20 mm
(0.02165 to 0.00787 inch)
Note: When you install a new top compression ring,
make sure that the word “TOP” is facing the top
of the piston. New top piston rings have a black
identification mark. The identification mark must be
on the left of the ring end gap when the top piston
ring is installed on an upright piston.
Width of top groove in the piston ................. Tapered
Width of second groove in new
piston ........ 2.56 to 2.58 mm (0.1008 to 0.1016 inch)
Width of third groove in new piston .. 3.02 to 3.04 mm
(0.1189 to 0.1197 inch)
(2) Intermediate compression ring
Piston pin
The shape of the intermediate compression
ring ....................................... Internal bevel in the
bottom edge with a tapered face
Diameter of a new piston
pin ..................................... 39.694 to 39.700 mm
(1.5628 to 1.5630 inch)
Width of intermediate compression
ring .... 2.47 to 2.495 mm (0.0972 to 0.0982 inch)
The clearance between a new intermediate
compression ring and the piston groove in a new
piston ..................................... 0.065 to 0.110 mm
(0.00256 to 0.00433 inch)
Ring gap ................................... 0.65 to 0.85 mm
(0.0256 to 0.0335 inch)
Note: When you install a new intermediate
compression ring, make sure that the word “TOP” is
facing the top of the piston. New intermediate rings
have a blue identification mark. The identification
mark must be on the left of the ring end gap when the
top piston ring is installed on an upright piston.
(3) The oil control ring
This document is printed from SPI². N

 English
English Espaol
Espaol Franais
Franais 阿拉伯
阿拉伯 中文
中文 Deutsch
Deutsch Italiano
Italiano Português
Português 日本
日本 韩国
韩国 български
български hrvatski
hrvatski esky
esky Dansk
Dansk Nederlands
Nederlands suomi
suomi Ελληνικ
Ελληνικ 印度
印度 norsk
norsk Polski
Polski Roman
Roman русский
русский Svenska
Svenska